Sharps Container Regulations: Your Guide
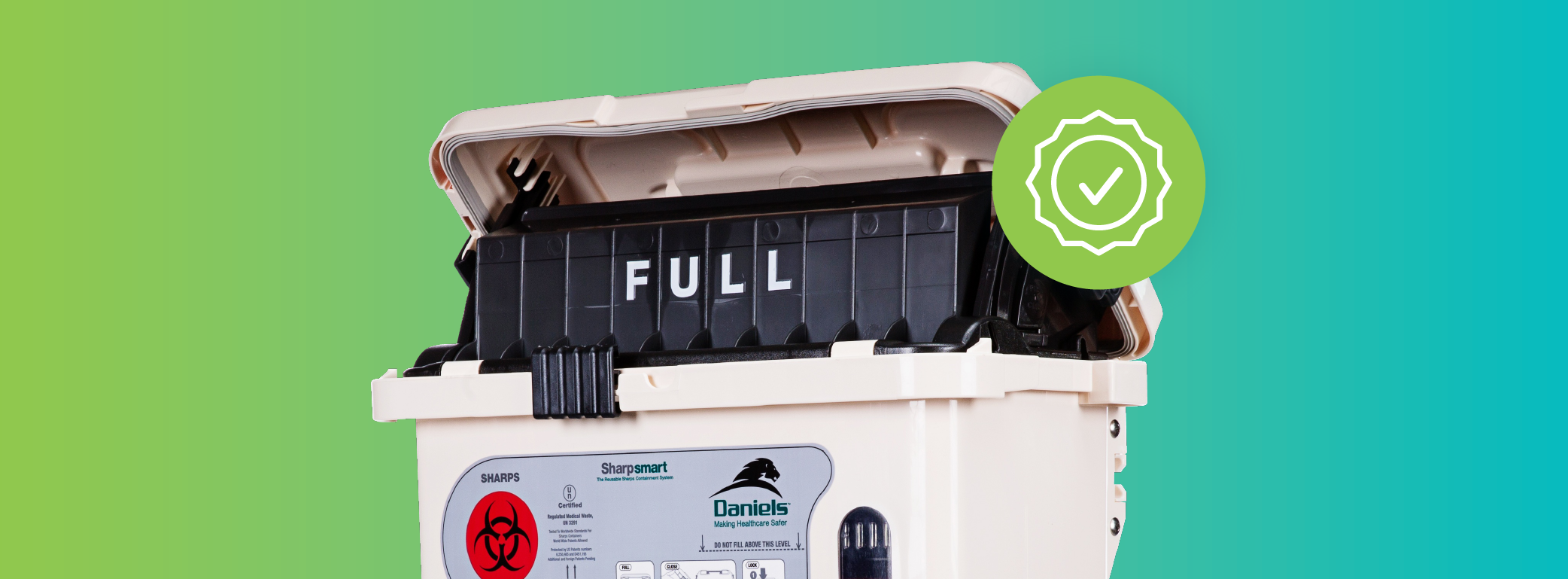

Every healthcare facility must manage sharps waste responsibly to ensure safety and comply with regulations. Sharps waste, which includes items like needles, syringes, and other sharp medical objects, poses significant health risks if not handled and disposed of properly. This guide covers the essential regulations and guidelines that healthcare facilities in the US must follow to ensure the safe and compliant disposal of sharps.
TOPICS WE WILL COVER:
1 / Understanding Sharps Containers
2 / The Importance of Safe Disposal and Compliant Handling of Sharps
3 / US Sharps Container Regulations — An Overview
4 / Sharps Container Regulations: Considerations
5 / Strategies For Sharps Injury Prevention
6 / Daniels Health – Sharpsmart Solutions
7 / Upgrade Your Facility With Daniels' Fully Compliant Sharps System
8 / FAQ - Sharps Container Regulations
Understanding Sharps Containers
Medical sharps are medical instruments that can puncture or cut the skin, such as needles, syringes, lancets, and scalpel blades. They are commonly used in healthcare settings for various procedures, including blood draws, injections, and surgeries.
Sharps containers are specially designed bins used by healthcare providers and facilities to dispose of these items safely. They are made from puncture-resistant materials and are labeled with hazard warnings to ensure safe handling and disposal.
The Importance of Safe Disposal and Compliant Handling of Sharps
Proper sharps disposal is crucial for protecting healthcare workers, patients, and the community from injury and infection. Improper handling of sharps can lead to needlestick injuries, which pose risks of transmitting infections such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Ensuring that sharps are disposed of in designated containers helps mitigate these risks and maintain a safe healthcare environment.
US Sharps Container Regulations — An Overview
In this section, we will detail the specific guidelines and regulations set forth by key government institutions, including the FDA, DOT, OSHA, and NIOSH, to ensure the safe and compliant disposal of sharps in healthcare settings.
FDA-Cleared Sharps Disposal Containers
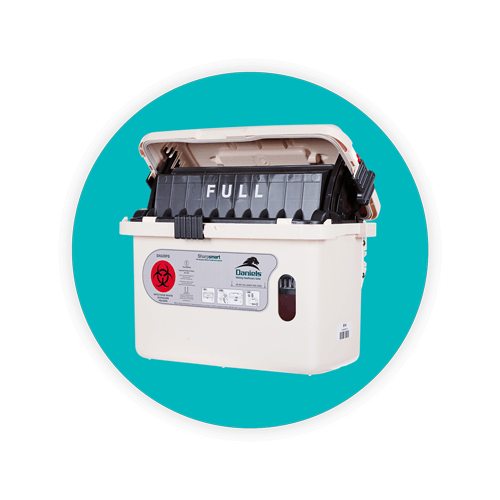
The US Food And Drug Administration (FDA) has established specific sharps container requirements to ensure safety and compliance.
An FDA-cleared sharps container must be made of heavy-duty plastic, feature a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, remain upright and stable during use, be leak-resistant, and properly labeled with a hazardous waste warning. Additionally, sharps disposal containers should be disposed of when they are three-quarters full, following community guidelines.
More information on FDA-cleared containers can be found on the FDA website.
DOT Sharps Container Regulations
The Department of Transportation (DOT) also has regulations concerning sharps disposal, particularly for containers transported off-site for disposal. These containers must be puncture-resistant and securely closeable to prevent leaks.
For sharps containers to be eligible for reuse, they must meet stringent requirements: they must be FDA-approved as reusable medical devices, permanently marked to indicate their suitability as reusable containers, and disinfected effectively based on the type of infectious substance they previously contained. Detailed information can be found on the HERCenter website.
OSHA Sharps Container Regulations
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth regulations to ensure the safe handling and disposal of sharps in a healthcare facility. These include:
-
Accessibility: Containers must be easily accessible and placed close to where sharps are used.

- Construction: Must be puncture-resistant, with leakproof sides and bottoms.
- Identification: Appropriately labeled or color-coded to indicate biohazardous contents.
- Design: Containers should be closable to prevent spillage and must remain upright.
- Maintenance: containers should be replaced routinely before they are overfilled to reduce injury risks.
- Handling Reusable Sharps Containers: These should not be manually opened, emptied, or cleaned in a way that exposes workers to needlestick injuries.
-
Storage of Contaminated Reusables: Ensure contaminated reusable sharps are stored in a way that does not require hand-reaching into containers.
More details can be found on the OSHA website.
NIOSH Sharps Container Guidelines
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) provides additional guidelines for sharps disposal containers:
- Functionality: Ensure containers are durable, closable, leak-resistant, and puncture-resistant.
- Accessibility: Position containers for easy access by users and maintenance staff; ensure portability if needed.
- Visibility: Containers should be clearly visible, showing fill level and bearing proper warning labels and color coding.
-
Accommodation: Design containers to be user-friendly: easy to store, assemble, and operate.
Further information is available on the Relias Media website.
Sharps Container Regulations: Considerations
State-specific regulations may impact facilities differently, so it's essential to stay informed about local requirements. Non-compliance with sharps disposal regulations can lead to significant consequences, including fines, legal action, and increased risk of exposure to infection or injury.
Strategies for Sharps Injury Prevention
Sharps-related injuries are a serious concern in healthcare settings. To reduce these needle stick injuries, facilities should:
To reduce these needle stick injuries, facilities should:
- Provide comprehensive training on sharps handling and disposal.
- Ensure proper placement of sharps containers to minimize the risk of accidental injuries.
- Utilize well-designed sharps containers that prevent overfilling and spillage.
-
Regularly audit and update sharps disposal practices to comply with the latest regulations.
Daniels Health — Sharpsmart Solutions
Daniels Health offers the Sharpsmart system, a comprehensive solution for sharps management. Sharpsmart containers are designed to enhance safety and compliance, featuring puncture-resistant materials, clear labeling, and secure lids. Daniels Health also provides comprehensive services, including training, support, and disposal, to ensure facilities meet all regulatory requirements. Their commitment to compliance, sustainability, and safety makes us a top choice for medical waste management.
Upgrade Your Facility with Daniels' Fully Compliant Sharps System
Adhering to sharps container regulations is crucial for ensuring the safety and compliance of your healthcare facility. Daniels Health offers a complete sharps management solution that meets all regulatory standards. Contact Daniels Health today for more information or to schedule a consultation and upgrade your facility with our fully compliant sharps system.
FAQ - Sharps Container Regulations
Do sharps containers need to be mounted?
The information regarding the mounting of sharps containers is based on general safety practices and recommendations from the FDA and OSHA guidelines. While there is no explicit regulation stating that sharps containers must be mounted, it is recommended to place them in stable and secure locations to prevent spills and ensure ease of access. Mounting is one way to achieve this stability and accessibility.
Where should a sharps container be placed?
The placement of sharps containers is guided by OSHA sharps container regulations, which state that containers must be easily accessible and placed as close as possible to the area where sharps are used. This is to minimize the need to transport sharps across a room and to ensure immediate disposal. Specific details can be found in the OSHA guidelines on bloodborne pathogens and needlestick prevention OSHA publication.
How often should sharps containers be changed out?
Sharps containers should be changed out when they are three-quarters full to prevent overfilling, as recommended by the FDA. This helps avoid spills and reduces the risk of needlestick injuries. Regular monitoring of the fill level and replacing containers before they become too full is crucial for maintaining safety. More details are provided in the FDA guidelines.
