How to Create a Biomedical Waste Operating Plan: Key Steps
Creating a comprehensive biomedical waste operating plan is crucial for healthcare facilities to ensure safety, regulatory compliance and efficient waste management practices.
TOPICS WE WILL COVER:
1 / Understanding Biomedical Waste and Its Categories
2 / The Importance of a Comprehensive Biomedical Waste Operating Plan
3 / Biomedical Waste Operating Plan Example
4 / Implementing Safety Protocols and Ongoing Employee Training
5 / Get Started with Comprehensive Biomedical Waste Solutions
 Understanding Biomedical Waste and Its Categories
Understanding Biomedical Waste and Its Categories
Biomedical waste (often referred to as biohazardous waste) is classified as any solid or liquid waste contaminated with blood, bodily fluids or other materials that could potentially spread infections.
Proper segregation of biomedical waste is critical to preventing cross-contamination of infectious materials and ensuring that the waste is treated appropriately. This also helps reduce overall disposal costs and ensures the facility complies with local and federal regulations.
This guide walks you through each step necessary to create an effective and compliant biomedical waste operating plan with expert consultation and guidance from a waste management vendor like Daniels Health.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Biomedical Waste Operating Plan
A biomedical waste operating plan is essential for maintaining compliance with healthcare waste disposal regulations, ensuring safety, and improving efficiency within a facility. These plans help minimize risks associated with the improper handling and disposal of medical waste, which could otherwise lead to public health concerns like cross-contamination, infection risks, and environmental damage.
Key Benefits of a Biomedical Waste Operating Plan
-
Regulatory Compliance: As biomedical waste generators, healthcare facilities must fulfill their cradle-to-grave responsibility to ensure the safe and proper handling of waste from generation to disposal. These facilities are subject to stringent local, state, and federal regulations regarding waste management. An effective biomedical waste operating plan ensures facilities remain compliant and avoid hefty fines.
-
Safety Measures: An operating plan outlines proper waste handling practices, reducing the risk of injuries or exposure to biohazardous materials for both patients and staff.
-
Environmental Responsibility: By reducing the amount of waste produced (and therefore the amount of waste requiring incineration), a well-structured waste plan supports sustainable healthcare practices, contributing to environmental protection.
Failure to implement a biomedical waste operating plan not only risks the health of the community, but can also result in legal repercussions and damage to a facility’s reputation if operations fall out of compliance with relevant regulations.
Biomedical Waste Operating Plan Example
Below is a biomedical waste operating plan example. Healthcare facilities can use it as a guide for improving safety, regulatory compliance and waste management efficiency.
 Step 1: Identifying and Categorizing Waste Streams
Step 1: Identifying and Categorizing Waste Streams
- Identify waste types: Conduct a waste audit to identify the different types of biomedical waste produced within the facility, including infectious waste, sharps, pharmaceutical waste, and more. Each category of waste has distinct handling requirements. For example, sharps waste requires puncture-resistant containers to prevent damage and injury.
- Segregate waste: Use color-coded waste containers to ensure proper segregation of waste. Proper segregation reduces the risk of contamination and lowers disposal costs by avoiding unnecessary classification of non-hazardous waste as hazardous. For more information, read our blog about color coding requirements for biomedical waste.
- Label appropriately: Clearly label containers to ensure that waste is stored, transported, and treated according to regulatory guidelines, such as those set by The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Department of Transportation (DOT) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Proper segregation prevents cross-contamination, reduces waste volumes requiring expensive hazardous waste treatment, and ensures compliance.
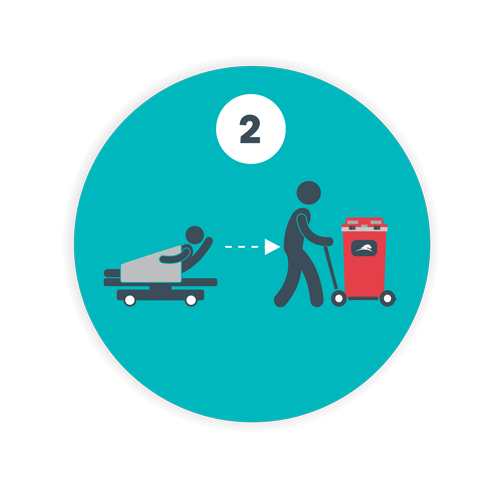 Step 2: Establishing Proper Containment and Storage Protocols
Step 2: Establishing Proper Containment and Storage Protocols
- Use appropriate containers: Biomedical waste should be stored in leakproof, puncture-resistant, and tamper-proof containers. For example, Daniels Health offers reusable medical waste containers that are designed for hands-free disposal with large apertures, counterbalanced doors, and passive overfill protection to ensure safe waste handling.
- Label containers: Ensure that all containers are labeled correctly with the facility name, address, and content type, which is essential for offsite transport and regulatory compliance.
- Secure storage: Waste should be stored in a designated area that is well-ventilated, secure, and inaccessible to unauthorized personnel. Waste should be removed promptly from biomedical waste storage areas to avoid potential health risks and comply with storage time limits.
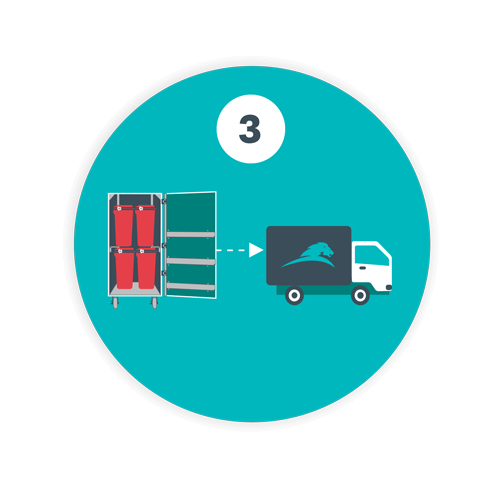 Step 3: Safe Removal and Transport of Waste
Step 3: Safe Removal and Transport of Waste
- Licensed transportation services: Facilities should partner with licensed waste haulers to ensure the safe and compliant removal of biomedical waste. These professionals are trained to follow all necessary protocols, ensuring that waste is safely transported to treatment and disposal facilities. Ideally, you should be able to track the journey of the waste removal vehicle once it leaves the facility.
- Documentation: Proper waste manifests must be maintained to record the journey of biomedical waste from the facility to the disposal site. This ensures transparency and compliance with local and federal waste management regulations.
- Ensure regulatory compliance: All waste removal and transportation must comply with regulations to avoid penalties and ensure public safety.
 Step 4: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Step 4: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
No waste management plan is complete without continuous monitoring and evaluation. By regularly assessing your biomedical waste operating plan, you can identify inefficiencies, mitigate risks, and ensure ongoing compliance.
Regular audits: Conducting regular audits of your facility’s biomedical waste management plan is a critical component of maintaining compliance and operational efficiency. These audits should evaluate various aspects of the plan, such as waste segregation, storage procedures, and disposal practices. Audits can also help identify any lapses in waste handling protocols that may put staff or patients at risk.
Employee feedback and engagement: One often overlooked aspect of continuous improvement is gathering feedback from the employees who handle and manage biomedical waste on a daily basis. These individuals (such as hospital staff) are in the best position to identify potential inefficiencies or hazards in the waste management system. By involving them in the audit process and encouraging them to share their experiences, healthcare facilities can foster a culture of proactive safety and compliance.
Leveraging technology for improvement: Healthcare innovation and new technologies, such as smart waste management systems, can provide real-time data on waste collection, storage, and removal processes. By integrating these technologies into your waste management plan, facilities can enhance their capacity to monitor and improve processes continuously.
Compliance reviews and future readiness: Continuous improvement isn’t just about current performance. Regular reviews of evolving regulations and industry standards are necessary to ensure that your biomedical waste operating plan is future-ready. As regulations change, facilities must adapt to new compliance requirements.
Implementing Safety Protocols and Ongoing Employee Training
Employee training is a key component of any biomedical waste management plan. Ensuring that employees are trained in waste handling, segregation, and safety protocols reduces the risk of contamination and improves overall facility safety.
Critical Aspects of Biomedical Waste Training
- Waste Segregation: Teach staff how to correctly segregate waste into the proper categories (and respective color-coded bins), such as sharps, infectious waste, and hazardous waste.
- Handling Procedures: To minimize exposure risks, employees should be trained to handle biohazardous materials properly and wear protective gear when needed.
- Emergency Response: Staff should be prepared to manage spills and other emergency situations involving biomedical waste.
Ongoing education is essential to maintaining a safe and compliant facility. Ensure your staff is up-to-date with the latest regulations and safety protocols by implementing regular training sessions.
 Get Started with Comprehensive Biomedical Waste Solutions
Get Started with Comprehensive Biomedical Waste Solutions
Creating a biomedical waste operating plan is the cornerstone of effective healthcare waste management. Daniels Health provides comprehensive solutions, from reusable containers to licensed waste disposal services, ensuring that healthcare facilities meet both their unique needs and regulatory requirements. By assessing each facility’s specific challenges, Daniels Health helps develop tailored plans that optimize compliance, safety, and efficiency.
Our clinically designed containers reduce exposure risks, while our transport services ensure waste is handled, transported, and disposed of responsibly. Partnering with Daniels Health allows facilities to streamline their waste management processes, reduce costs, and minimize their environmental footprint. Contact us today to learn more about improving your biomedical waste operating plan with innovative, reliable solutions.
Let's Talk!
Your time is valuable, and we don’t want to play hard to get. You can either phone us directly on the details listed on our contact page, or feel free to fill out this short form and one of our team members will get back to you as quickly as possible.
